- July 26, 2024
- Abi Therala
- 0
The Comprehensive Guide to use LLM Models for Operational Success
In the fast-paced, data-driven world of operations, efficiency is paramount. The constant juggling of system monitoring, incident response, troubleshooting, and routine maintenance demands innovative solutions. Large Language Models (LLMs), a cutting-edge subset of artificial intelligence, are emerging as a transformative force for ops teams, offering the potential to streamline workflows, automate tasks, and augment human decision-making. Let’s explore the technical intricacies of how in-house LLM models can revolutionize your operational capabilities and enhance operations research.
Understanding the Power of the Largest Language Models
At their core, large language models are sophisticated algorithms trained on massive datasets comprising text and code. This extensive training equips them with the ability to understand natural language, generate human-like text, translate languages, and even produce creative content like poetry or code. Their aptitude for processing and interpreting vast amounts of information makes them a potent asset for complex operational environments.
In-House LLMs: The Key to Operational Excellence
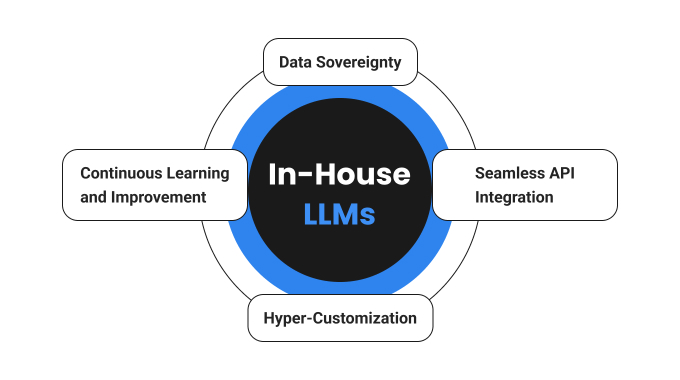
While general-purpose LLM models like ChatGPT showcase impressive capabilities, fine-tuning an in-house large language model on your company’s specific data offers unparalleled advantages for operational teams:
- Data Sovereignty: Sensitive operational data, such as system logs, incident reports, proprietary code, and confidential customer information, remains securely within your organization’s infrastructure, mitigating the risk of data leakage or unauthorized access.
- Hyper-Customization: Training the LLM on your internal documentation, code repositories, knowledge bases, and historical incident data allows it to develop a deep understanding of your unique terminology, workflows, and system architecture.
- Seamless API Integration: Easily integrate the LLM with your existing operational tools, including ticketing systems, monitoring platforms, configuration management tools, and communication channels, creating a cohesive and efficient ecosystem.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: Regularly fine-tune the model with new data, feedback from users, and evolving operational requirements, ensuring its accuracy, relevance, and effectiveness continuously improve over time.
Technical Applications of LLMs in Ops
- Intelligent Process Automation:
- Repetitive, manual tasks can bog down operational teams and hinder productivity.
- In-house LLMs can automate various processes, such as data entry, report generation, invoice processing, and even complex decision-making workflows based on predefined rules and historical data.
- Enhanced Decision-Making and Analysis:
- Making informed decisions often requires sifting through vast amounts of data and identifying patterns or trends.
- LLM models can rapidly analyze data from diverse sources, generate insightful summaries, and even provide recommendations based on historical patterns, empowering teams to make faster, data-driven decisions.
- Streamlined Communication and Collaboration:
- Effective communication is essential for seamless operations, but miscommunication and information silos can hinder progress.
- LLMs can facilitate communication by summarizing lengthy documents, drafting emails, and even acting as virtual assistants to answer questions or provide information on demand.
- Predictive Analytics and Forecasting:
- Anticipating future trends and potential challenges is crucial for proactive decision-making and resource allocation.
- LLMs can analyze historical data and identify patterns to forecast demand, predict customer behaviour, and identify potential risks or opportunities.
- Knowledge Management and Expertise Sharing:
- Capturing and sharing institutional knowledge is essential for organizational learning and growth.
- Large language models can be used to create centralized knowledge repositories, generate summaries of complex information, and facilitate knowledge sharing across teams, ensuring that valuable expertise is not lost.
- Intelligent Alert Correlation and Triage:
- Modern IT environments generate a deluge of alerts, often overwhelming ops teams and obscuring critical issues.
- In-house LLMs can analyze alert patterns, correlate events across different systems, and prioritize incidents based on their severity, impact, and historical context, streamlining incident response and reducing alert fatigue.
- Automated Root Cause Analysis (RCA):
- Identifying the root cause of complex incidents traditionally involves manual investigation, expert knowledge, and considerable time investment.
- LLM models can rapidly analyze vast amounts of system logs, configuration data, historical incident reports, and even code repositories to pinpoint potential root causes, significantly accelerating the RCA process and minimizing system downtime.
- Knowledge Base Augmentation and Intelligent Search:
- Maintaining comprehensive and up-to-date knowledge bases is an ongoing challenge for ops teams, hindering efficient troubleshooting and knowledge sharing.
- Large language models can ingest and organize vast amounts of technical documentation, wikis, and other knowledge sources. They can generate concise summaries, answer complex questions posed in natural language, and even provide contextual recommendations, empowering ops teams with quick and accurate access to critical information.
- Automated Incident Reporting and Communication:
- Clear and timely communication is essential during incident response, but manual reporting can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
- LLMs can automate the generation of incident reports, summarizing key details, timelines, and actions taken. They can also draft communications to stakeholders, ensuring consistent and accurate information dissemination.
- ChatOps and Intelligent Virtual Assistants:
- Ops teams often rely on chat platforms for collaboration and communication.
- Integrating large language models into these platforms can enable intelligent virtual assistants that can answer questions, provide troubleshooting guidance, and even execute commands, streamlining communication and boosting productivity.
The Path Forward: Embracing AI-Augmented Ops
The convergence of large language models and IT operations represents a paradigm shift in the way teams work. By harnessing the power of AI to automate tasks, augment decision-making, and unlock hidden insights, organizations can achieve unprecedented levels of operational efficiency, agility, and resilience.
The adoption of LLMs in IT operations presents a range of ethical considerations that require careful attention. It’s crucial to ensure that these models are trained on unbiased data to prevent perpetuating discrimination or unfair outcomes. Additionally, the explainability of LLM decision-making processes is essential, particularly in critical operational scenarios. Human oversight remains vital for validating LLM outputs and making final decisions. By fostering a culture of transparency and responsible AI practices, organizations can leverage the power of LLMs while mitigating potential ethical risks.
Age of AI-Augmented Teams
As LLMs continue to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated applications in the realm of operations, including:
- Autonomous Incident Resolution: LLMs may eventually be able to resolve certain types of incidents autonomously, freeing up ops teams to focus on more complex and strategic tasks.
- AI-Driven Capacity Planning: LLMs could analyze historical usage patterns and predict future demand, enabling proactive capacity planning and resource allocation.
- Enhanced Security Operations: LLMs could play a key role in threat detection, incident response, and vulnerability management, bolstering an organization’s security posture.
The future of IT operations is AI-augmented. By embracing LLMs and integrating them strategically into your operational workflows, you can empower your team to navigate the complexities of modern IT environments with confidence, efficiency, and innovation.